Solar panels can save a lot of money, but the technology remains mysterious to most of us. We all know solar panels create energy, but how exactly do they convert sunlight into electricity? Read on to learn more about the technology of solar cells and panels and how they connect you to energy independence and future savings.
How a Solar Panel Works
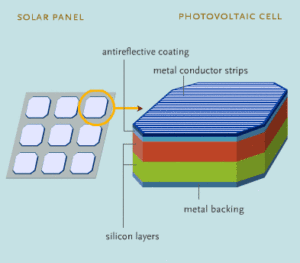
Solar panels are arranged into arrays or ordered series of panels on a rooftop. Each panel consists of protective glass, a conductive metal contact, two layers of silicon cells, and a conductive metal base. Each solar cell contains one positive and one negative layer of silicon, also called P-type and N-type silicon. When layered, some of the electrons from either side will come together, which creates an electric field. This is because the opposite impurities in the two layers of silicon, created by adding phosphorus and boron, cause electrons to flow.
When sunlight strikes the cell, it creates free-roaming electrons and holes in either layer of silicon, which are then forced back into their proper layer. Connecting a circuit between the two layers then allows for the driving of excess electrons and holes together, creating an electric current. From here, the electricity is converted from this direct current, into what is known as alternating current, the type of electricity used by most homes.
Energy Conversion and Your Home

An inverter converts DC electricity to alternating current (AC) for use in the home. This is either done with a single inverter, or individual micro-inverters, which connect to each panel. The micros are often considered to be superior, as they take out less of the array when they fail, and they provide panel-level monitoring. This monitoring is important because it allows solar homeowners to ensure that their system is operating at the highest efficiency possible. Read more about inverters to find out the best option for you.
After this, the home uses the generated power first. Nothing else within the home needs to be changed to make this possible, since the energy you generate is the same as that provided by the utility company. Because of the varying nature of energy usage, net metering allows for the crediting and compensation of solar homeowners. When there is not enough sun, (or it is nighttime), energy from the grid supplements. During the day when no one is home the AC power the home does not use is sent back into the grid for neighbors and other customers to use. Read more about net metering to learn more.
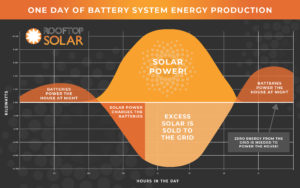
Energy Control and Batteries
The system described above equips homeowners with the ability to control their energy usage by using the grid as a sort of battery. Some homeowners decide to take things a step further by installing a hybrid system with batteries and the grid. This is because it allows you to have complete control over when you pull from the grid, when you charge your batteries, and when you pull from the batteries. This gives you complete control over your utility’s rate system on time-of-use plans, and will often allow you to monitor your power generation even more closely, as you create a total hybrid system.
Because energy offset is done on a year-round basis, most homeowners will still choose to be on the grid even if they choose battery backup. As battery technology improves, however, homeowners are finding more and more ways to avoid the power company.
Understanding more about the technical side of solar allows for a better understanding of the financial payback. This brilliant technology can be used to power our lives, and avoid those bills, and it is as good a time as ever to invest. Many homeowners can save from day one, so find out today how this technology can work for you!